This article was originally posted on Daily.Dev .
Welcome to part 2 of this article series where I show you how to create a killer GitHub profile!
If you haven't read part 1, click here and follow along before reading this article.
In the previous article, I documented my process for building out my README.template.md file.
I added sections for an intro, latest blog posts, pinned repositories, GitHub stats, skills and a skeleton section for an Office quote.
In this second article and final issue in this series, I will add the dynamic content injection and will get you familiar with GitHub Action workflows!
Prepping for the Magic
Now that the README.template.md file is complete, I started working on the fun part — the dynamic injection.
There are two main portions of the file that need dynamic content injection — the blog section and The Office quote section.
Listing recent blog articles is the easy part — that functionality was built for me (see the linked tutorial in the previous article) and I just needed to hook up the workflow.
The Office quote, however, required a little more effort because I needed to create the functionality myself. For something simple like making an API request, I decided to create a simple node script to handle the operation.
At the root of my repository, I created a new file called index.js.
The index.js File
There are four steps this file needs to complete:
- Create a variable to reference the
README.template.mdfile - Make the request to The Office API
- Look through the
README.template.mdcontent and replace the static patterns ({office_quote}&{office_character}) with the dynamic result of the API request - Create/replace the contents of the
README.mdfile with the updatedREADME.template.mdreference variable.
Thinking about these responsibilities, I imported the required dependencies in the index.js file.
require("isomorphic-unfetch");
const { promises: fs } = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
To complete step one, I declared an async function called main , grabbed a reference to the template file and placed it in variable named readmeTemplate.
async function main() {
const readmeTemplate = (
await fs.readFile(path.join(process.cwd(), "./README.template.md"))
).toString("utf-8");
}
main();
The next step is to make the API request. Below the readmeTemplate variable, I created a request to The Office API and assigned the result to a variable called office_quote.
const office_quote = await (
await fetch("https://officeapi.dev/api/quotes/random")
).json();
The third step is to replace the patterns in the template file with the dynamic content retrieved from The Office API.
const readme = readmeTemplate
.replace("{office_quote}", office_quote.data.content)
.replace("{office_character}", `- ${office_quote.data.character.firstname} ${office_quote.data.character.lastname}`)
Finally, I create/replace the contents of the README.md file with the readmeTemplate variable.
await fs.writeFile("README.md", readme);
At this point I could run node . at the root of my repository and the index.js file worked its magic. Opening the README.md file, I saw the dynamic quote at the bottom of the file.
If you want to reference my full index.js file, click HERE.
Creating the Workflow
The index.js file, by itself, isn't very helpful because I need to run the file every time I want the quote to update. How do I have the file run automatically? GitHub Actions.
Setting up a GitHub Action workflow is easy if I have the correct file-structure; I don’t need to do anything on GitHub’s website to get it working.
I created the following directories and file at the root of my repository:
- root
- .github
workflows
dynamic-injection-workflow.yml

Next, I opened the dynamic-injection-workflow.yml file, named the workflow and added some instruction on when the workflow should run. I scheduled a cron job to run this workflow every hour so new blog posts are fetched frequently and visitors get a new Office quote with regular cadence.
name: Dynamic README injection
on:
schedule: # Run workflow automatically
# This will make it run every hour
- cron: "0 * * * *"
# Run workflow manually (without waiting for the cron to be called), through the Github Actions Workflow page directly
Now that I have basic structure in the workflow, I need to define jobs for the workflow to run.
The order of these jobs matter (more on that in a second), so I created the first job to get an Office quote.
name: Dynamic README injection
on:
schedule: # Run workflow automatically
# This will make it run every hour
- cron: "0 * * * *"
# Run workflow manually (without waiting for the cron to be called), through the Github Actions Workflow page directly
jobs:
get-office-quotes:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Let the magic happen
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: 14.6.0
- run: yarn
- run: node .
- name: Add to git repo
run: |
git config pull.rebase false
git pull
git add .
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "Your E-Mail"
git commit -m "[Automated] README updated with new Office quote!"
- name: Push
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
Notice that the job runs node . at the root of the project, causing the index.js file to execute, fetch the quote, and take everything in the README.template.md file and copy it over to the README.md file. This, in and of itself, isn't enough for the updated information to show up on my profile. I need to commit and push the changes to my repository, which is why I added he Add to git repo step.
Now that the README.md file contains an Office quote and everything else in the README.template.md file, I can run the final job to fetch my updated blog posts (Remember, the README.md file now contains the static blog post pattern we created in the previous article).
name: Dynamic README injection
on:
schedule: # Run workflow automatically
# This will make it run every hour
- cron: "0 * * * *"
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
get-office-quotes:
# job steps
...
update-readme-with-blog:
needs: get-office-quotes
name: Update this repo's README with latest blog posts
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- uses: gautamkrishnar/blog-post-workflow@master
with:
# Replace this URL with your rss feed URL/s
feed_list: "https://braydoncoyer.hashnode.dev/rss.xml"
Because of the way that Gautam Krishna R's GitHub action works, this job must run after I inject an Office quote — if it doesn't, it will write over the content in the README.md file and delete the quote. Thankfully, GitHub Actions has a needs property that I added to the workflow so that it only activates after the get-office-quotes workflow has completed its steps.
The dynamic-injection-workflow.yml file is now complete. I committed my changes and pushed them to my GitHub profile repository.
GitHub recognized that I added a workflow and I can see it listed under Actions > All workflows.

To manually run the workflow and to test to see if it was working, I clicked on the 'Run workflow' dropdown button and then had the workflow run on the main branch. (Remember, the cron job will run this automatically every hour.)

After the workflow successfully completed both jobs, I went back to my profile to see the final result!
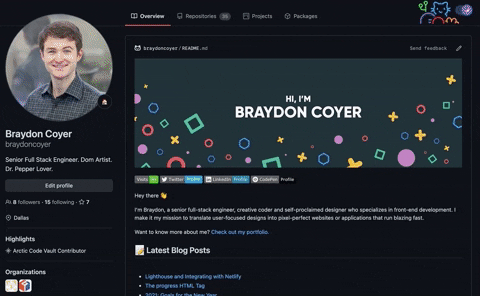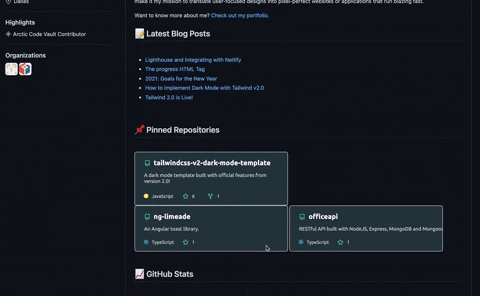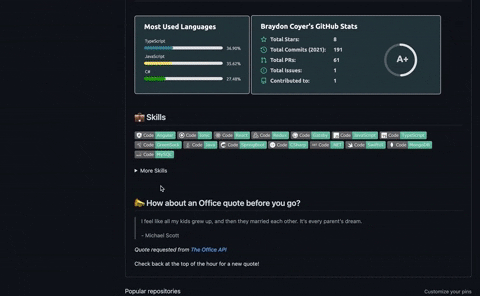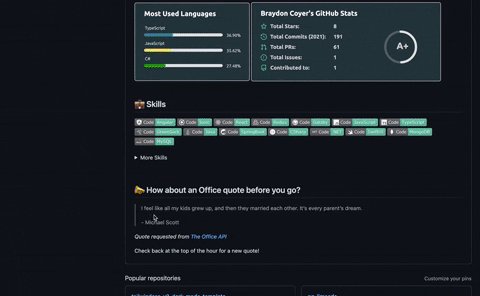
Conclusion
There we go! You should now have all of the tools required to make a killer GitHub profile README!
Don't forget that your profile on GitHub is like your portfolio -- use it as a platform to highlight what makes you unique as a developer!
When you've finished created your own GitHub profile README, send me a link in the comments below! I'd love to check it out!
Thanks for reading! If you liked this article and want more content like this, subscribe to my newsletter and make sure to follow me on Twitter!
